Types of Soil in India and Their Importance in Agriculture
India is blessed with diverse soils that play a key role in determining the crops grown in different regions. Understanding soil types is crucial for farmers to choose the right crops, fertilizers, and soil management practices. Here’s a detailed look at the
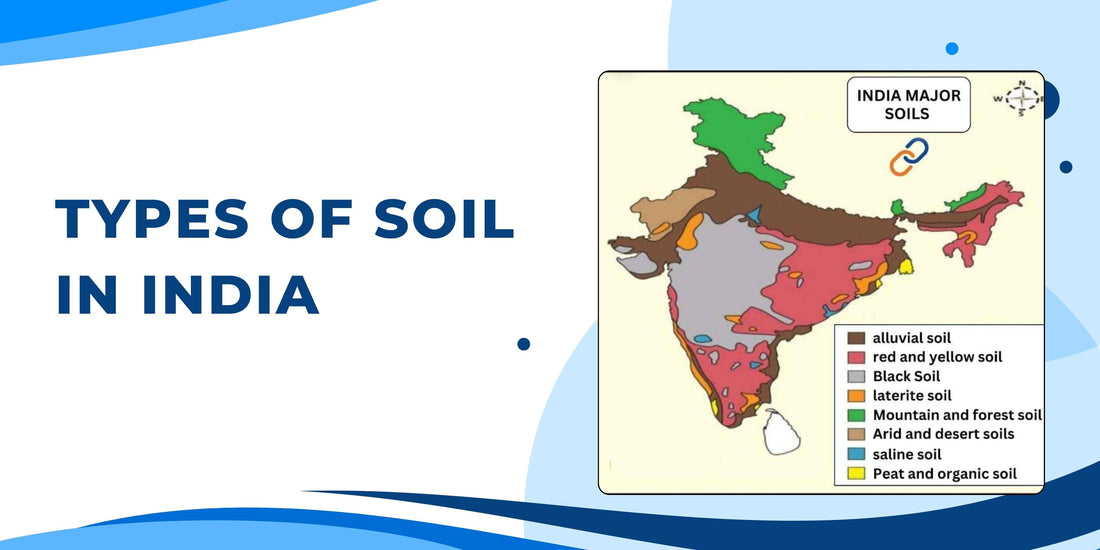
Major soil types found in India:
1. Alluvial Soil
- Region: Northern Plains, river valleys of Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus.
- Features: Fertile, rich in potash and lime but low in nitrogen.
- Best Crops: Wheat, rice, sugarcane, maize, pulses, oilseeds, and vegetables.
2. Black Soil (Regur Soil)
- Region: Deccan Plateau – Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, parts of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
- Features: High moisture retention, rich in lime, iron, magnesium; poor in phosphorus and nitrogen.
- Best Crops: Cotton (hence called “cotton soil”), soybean, pulses, groundnut, and citrus fruits.
3. Red Soil
- Region: Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand.
- Features: Rich in iron, but poor in nitrogen, phosphorus, and humus.
- Best Crops: Millets, pulses, groundnut, tobacco, potato, and fruits like mango.
4. Laterite Soil
- Region: Western Ghats, parts of Odisha, West Bengal, Assam, and Meghalaya.
- Features: Rich in iron and aluminum, poor in organic matter, nitrogen, and calcium. Needs proper fertilizers for productivity.
- Best Crops: Tea, coffee, cashew, rubber, and coconut.
5. Desert Soil (Arid Soil)
- Region: Rajasthan, parts of Haryana and Gujarat.
- Features: Sandy, saline, low in nitrogen and organic matter, but rich in calcium carbonate.
- Best Crops: Barley, millet (bajra), maize, pulses, and guar. With irrigation, cotton and wheat can also be grown.
6. Mountain Soil (Forest Soil)
- Region: Himalayan regions, Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and NE states.
- Features: Varies with altitude; rich in humus, but poor in nutrients in some areas.
- Best Crops: Tea, coffee, spices, fruits (apple, pear, plum), and medicinal plants.
7. Saline and Alkaline Soil
- Region: Parts of Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar.
- Features: Contains excess salts, poor in fertility. With proper gypsum and organic inputs, fertility can be restored.
- Best Crops: Rice, barley, sugar beet (after soil treatment).
Conclusion
Different soils in India support different crops. With proper soil testing, use of organic matter, and balanced fertilizers, farmers can improve productivity and profitability. Choosing the right agri-inputs for your soil type ensures better yield and sustainable farming.
